In all plant-based diets, protein is not the only essential nutrient. Trace elements, lipids, iron, calcium, vitamins and minerals are very important too.
 LIPIDS
LIPIDS
Lipids (fatty acids) are essential. They are a source of energy for the muscles and the brain. They feed it, as well as the retina.
Eaten in too large quantities or of poor quality, they transform into adipose tissue and triglycerides (just to be ready in case of sudden and brutal starvation^^) and raise the bad cholesterol level.
There are 3 types of fatty acids:
 Saturated fats
Saturated fats  : often of animal origin: butter, milk, meat but also coconut or palm oil. In large quantities they increase the level of bad cholesterol
: often of animal origin: butter, milk, meat but also coconut or palm oil. In large quantities they increase the level of bad cholesterol Mono-unsaturated fats (Omega 9)
Mono-unsaturated fats (Omega 9)  : They benefit to the cardio-vascular function.
: They benefit to the cardio-vascular function. Poly-unsaturated fats (Omega 6 and 3)
Poly-unsaturated fats (Omega 6 and 3)  : protectors of the cardio-vascular function, they decrease the blood’s level of lipid, regulate the arterial pressure, maintain the platelet and vascular functions and control the inflammation.
: protectors of the cardio-vascular function, they decrease the blood’s level of lipid, regulate the arterial pressure, maintain the platelet and vascular functions and control the inflammation.
Finally, the trans fats are part of the unsaturated fats. They come from industrial processes and transformations. Example: transforming vegetal oils into margarine. We can find them in prepared meals and processed foods. Those fatty acids are by far the most dangerous for the health.
RECAP:
-
 Saturated fatty acids = coconut oil, palm oil
Saturated fatty acids = coconut oil, palm oil -
 Mono-unsaturated fatty acids = olive oil, nuts, peanuts, avocado, hazelnuts
Mono-unsaturated fatty acids = olive oil, nuts, peanuts, avocado, hazelnuts  Poly-unsaturated fatty acids = flax seeds and some vegetal oils and nuts
Poly-unsaturated fatty acids = flax seeds and some vegetal oils and nuts
 OMEGA 3-6 FOCUS
OMEGA 3-6 FOCUS
Omega 3 are useful for the good operation of the brain, the retina and to the fluidity of the blood among other things.
Omega 6 are important for the growth, for the blood coagulation and for the impermeability of the skin.
But there is a certain ratio to respect.
Usually, our consumption of omega 3 must but around 20/25% of what we get of omega 6. This ratio is almost never respected, and this, in every type of population because we eat much more omega 6.Therefore, the challenge is to increase our consumption of omega 3 to get closer to the objective.
As vegans/vegetarians, we can find omega 6 into:
- Sunflower oil, soy oil, corn oil, sesame oil, grape seed oil …
- Pumpkin seeds
- Peanuts and processed foods (crisps etc…)
And omega 3 into:
- Colza oil, nuts and flax seeds oils
- Flax seeds, chia seeds, nuts, hemp, cashews
 IRON
IRON
As explained “Fears and popular misconceptions”, there are 2 types of iron.
– Haem iron is the one provided by animals. It has a bio availability of 25% which eases its absorption by the human body.
– Non haem iron is the one we can find in plants and its bioavailability is closer to 5%. Better explained, it is less easy for the body to absorb it
However, the variation of your level of iron when switching to a plant-based diet will be your own (see Fears and popular misconceptions page).
There are, foods that can help you get more iron, and others that you should avoid or that should be consumed outside of the digestive periods
to help reduce the potential drop in your iron levels. There are also interesting combinations of foods to make :
There are also interesting combinations of foods to make :
FOOD RICH IN IRON + FOOD RICH IN VITAMIN C
Indeed, vitamin C boosts the iron absorption during the digestive process.
The objective is to combine these ingredients in the same meal.
 Foods naturally rich in iron:
Foods naturally rich in iron:
- Algaes
- Cocoa
- Sunflower seeds, sesame, flax seeds, pumpkin or chia seeds
- Dried tomatoes and dried apricots
- Oats
- Roasted hazelnuts, cashews
- …
 Foods rich in vitamin C:
Foods rich in vitamin C:
- Citruses (orange, lemon, grapefruit)
- Guava, papaya, mango (well those 3 are not very local)
- Kiwi, strawberry, blackcurrant, pineapple
- Broccoli, pepper, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower
- …
 Foods that hold iron absorption:
Foods that hold iron absorption:
- Tannins and polyphenols of tea and coffee, wine, yolk
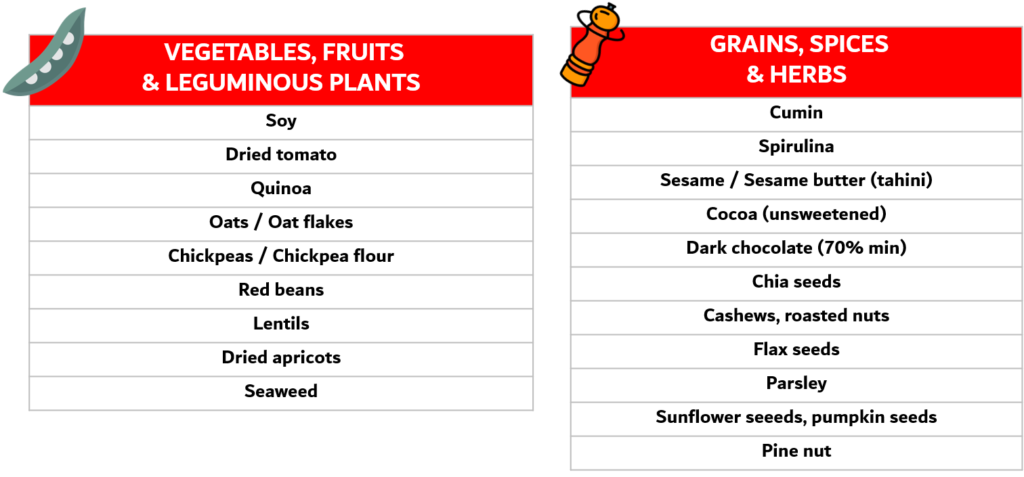
Here is a list of plant-based foods well-known for their high level of iron.
FYI, we have tried to look for their respective iron rates by crossing different sources of information. However, precise data is hard to find and can change from one source to the other. So don’t take as certain the numbers below they are only indications but please note that these foods are rich in iron and that including them into your diet can only do good.
 CALCIUM
CALCIUM
As we saw in the “Fears and popular misconceptions” page, the benefits of animal calcium consumption are not proven or at least are being questioned. Indeed, wide regions of the world consume very few of it and those populations have a lower bone fractures rate at advanced ages than in the western hemisphere.
Once more, it looks like we are facing an unknown field of nutrition science.
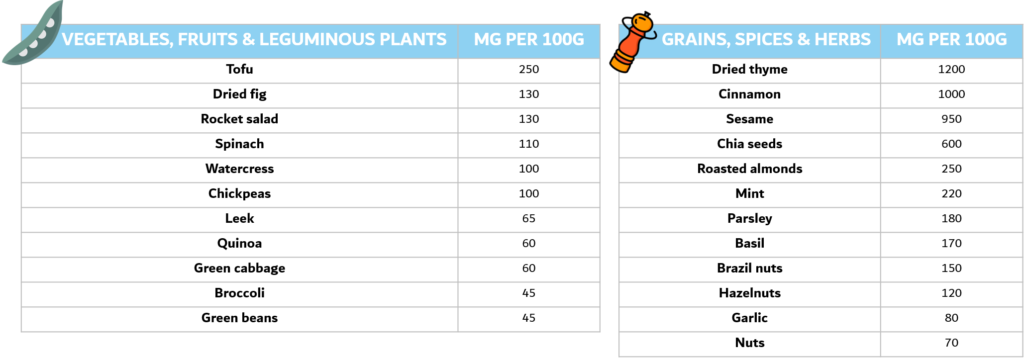
Here is a list of plant-based foods well-known for their high level of calcium.
FYI, we have tried to look for their respective calcium rates by crossing different sources of information. However, precise data is hard to find and can change from one source to the other. So don’t take as certain the numbers below they are only indications but please note that these foods are rich in calcium and that including them into your diet can only do good.
ZINC / VITAMINS
Read our posts about those topics in our page
« Fears and popular misconceptions»
